Lightweight regulatory standard pollutants refer to various harmful substances such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, volatile organic compounds, etc. produced in the emissions of automobiles, ships, industries and households. The emission of these pollutants has caused serious impacts on the environment and human health, such as reduced air quality, climate change, acid rain, etc. As a result, various emission standards have been developed worldwide to limit the impact of these pollutants.
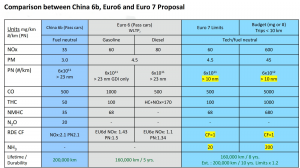
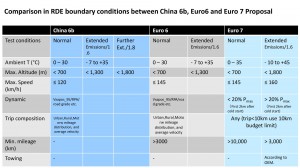
Vehicle emissions standards are one of the most important standards to limit vehicle emissions. At present, the world’s most stringent vehicle emission standard is the European Union’s Euro 6 standard, which limits the emission of nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, non-methane hydrocarbons and other pollutants. Other countries and regions have also developed similar emission standards, such as the Tier 4 standard in the United States and the China VI standard in China.
The global regulation of light regulatory standard pollutants varies from region to region, but in general, international cooperation and standardization organizations play an important role. Here are some of the main regulatory bodies and standards:
1. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): ISO develops globally harmonized environmental standards to help governments and enterprises reach international standards.
2. European Union (EU): The European Union regulates light regulatory standard pollutants through EU directives and regulations. For example, EU Directive 2000/53/EC is a regulation on the recycling, reuse and disposal of automobiles and components.
3. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): The EPA sets strict environmental regulations and standards to ensure that air, water, land, and biodiversity are protected. For example, the EPA sets vehicle emissions standards and fuel efficiency standards.
4. China’s Ministry of Environmental Protection: China’s Ministry of Environmental Protection is responsible for formulating and implementing environmental policies, including the regulation of light regulatory standard pollutants. For example, China has implemented the Passenger Car Fuel Consumption Limit standard, which limits vehicle fuel consumption to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
In order to meet emission standards, various vehicles and equipment need to install emission control devices, such as three-way catalytic converters and diesel particulate filters. These devices reduce pollutant emissions and improve the fuel efficiency and power performance of vehicles and equipment.
CAT Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the research and development, production, sales and related technical services of motor vehicle pollutant emission control catalysts, with a registered capital of 20 million yuan, with leading core technology, strong research and development capabilities, high-quality after-sales service and management and operation experience of various projects, and strive to build the most professional and excellent professional team.
Light regulatory standard pollutants are not static, with the continuous advancement of environmental protection technology and the update of international environmental protection regulations, corresponding adjustments and corrections are required. Countries should update relevant regulations according to the actual situation to better protect the environment and human health.
In general, the supervision of light regulatory standards and pollutants is gradually strengthening worldwide, and the trend of international cooperation and standardization is becoming more and more obvious.
Post time: Aug-09-2023